Two basic forms of surface primitive are provided for in the GINO library, the Spline surface and the Bezier surface. The basic difference between the two forms is the interpretation of the supplied data points. In the same way as the corresponding curve types, Spline surfaces pass through all the supplied data points, whereas the Bezier surface only aligns with the supplied data at the start and end of the surface. The supplied data can therefore be seen as control points affecting the shape of the surface only.
Both forms of surface are constructed using one or more sets of user supplied 3D data/control points from which are interpolated a smooth set of points that represent the interior/edges of the surface.
In other words, the complexity of the surface is not determined by the number of points supplied in the data arrays, but the values set in the optional arguments gUComp and gVComp.
The following sections describe the drawing of each of the surface primitives.
The basic Spline surface is constructed from a grid of 3D data points, with an optional complexity specification of the final surface:
gDrawSplineSurface(nx, ny, mesh, [gUComp, gVComp])Where nx and ny are the dimensions of the 2 dimensional array of data points of type GPOINT3 passed in mesh.
The setting of gUComp and gVComp define the complexity of the surface in terms of the number of facets generated across the complete surface in each direction. The values of gUComp and gVComp may however be rounded down internally as the actual number of facets must be a multiple of the number of data points so that the surface passes through each of them as supplied. The default setting for these arguments is 4*(nx-1) and 4*(ny-1) respectively
No end conditions can be set for spline surfaces but special attention is given to data that is closed in the 'U' direction such that a smooth join is automatically maintained at the junction. The routine gSetSplineTension() can also be used to control the tension of the spline surface in the same manner as for curves (see Spline tension).
A closed spline surface generated from 25 data points is shown in the figure below with the code following:
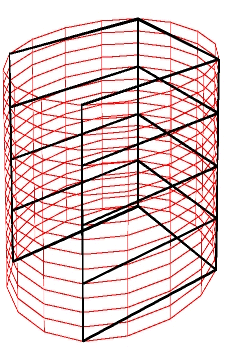 |
Spline Surface |
[C/C++] #include <math.h>
#include <gino-c.h>
#define NX 5
#define NY 5
#define CLOSED 1
int main ()
{ GDIM paper;
GLIMIT3 viewport = {-100.0,100.0,-100.0,200.0,0.0,5000.0};
GLIMIT limits = {0.0,0.0,0.0,0.0};
/* Define control points */
GPOINT3 pxyz[NX][NY];
int i,j,ip;
float s,x,y,z;
float spten=0.0;
/* Initialise Gino and Device */
gOpenGino();
xxxxx();
/* Set up 3D Viewport to fit whole drawing area */
gEnqDrawingLimits(&paper,&ip);
limits.xmax = paper.xpap;
limits.ymax = paper.ypap; gSetViewport3D(&viewport,&limits);
/* Define View */
gDefinePerspView(100.0,200.0,800.0,-0.1,-0.2,-0.8,1200.0);
gUpdateView();
/* Compute surface grid */
/* Define the elliptic cylinder - to show the difference a closed and */
/* open surface choose exact or approximate values of Pi below */
for (i=0; i<NX; i++) {
if (CLOSED)
s = 2.0*3.1415926*i/(NX-1);
else
s = 2.0*3.14*i/(NY-1);
x = sin(s);
z = 2.0*cos(s);
for(j=0; j<NY; j++) {
y = -1.0 + 2.0*j/(NY-1);
pxyz[i][j].x = x*50;
pxyz[i][j].y = y*50;
pxyz[i][j].z = (z+1.0)*50;
}
}
/* Set Hollow Fill Style */
gSetFacetFillStyle(GHOLLOW);
/* Compute spline surface after setting the spline tension */
gSetSplineTension(spten);
gSetLineColour(GRED);
gDrawSplineSurface(NX,NY,(GPOINT3 *)pxyz);
/* Draw control points mesh */
gSetLineColour(GBLACK);
gSetLineWidth(1.0);
for(i=0; i<NX; i++) {
gMoveTo3D(pxyz[i][0].x,pxyz[i][0].y,pxyz[i][0].z);
gDrawPolylineTo3D(NY,pxyz[i]);
}
for(i=0; i<NY; i++) {
gMoveTo3D(pxyz[0][i].x,pxyz[0][i].y,pxyz[0][i].z);
for(j=1; j<NX-1; j++)
gDrawLineTo3D(pxyz[j][i].x,pxyz[j][i].y,pxyz[j][i].z);
}
gFlushGraphics (); /* Close down */
gSuspendDevice();
gCloseGino();
}
[F90] use gino_f90
parameter (nx=5,ny=5)
type (GDIM) :: paper type (GLIMIT3) :: viewport = GLIMIT3(-100.0,100.0,-100.0,200.0,0.0,5000.0)
type (GLIMIT) :: limits = GLIMIT(0.0,0.0,0.0,0.0)
! Define control points
type (GPOINT3) :: pxyz(nx,ny) !
! Initialise Gino and Device
call gOpenGino
call gWogl !
! Set up 3D Viewport to fit whole drawing area
call gEnqDrawingLimits(paper,ip)
limits%xmax = paper%xpap
limits%ymax = paper%ypap
call gSetViewport3D(viewport,limits) !
! Define View
call gDefinePerspView(100.0,200.0,800.0,-0.1,-0.2,-0.8,1200.0)
call gUpdateView !
! Compute surface grid
! Define the elliptic cylinder - to show the difference a closed and
! open surface choose exact or approximate values of Pi below
iclose=1
do i = 1, nx
if (iclose .eq. 1) then
s = 2.0*3.1415926*(i-1)/(nx-1)
else
s = 2.0*3.14*(i-1)/(nx-1)
end if
x = sin(s)
z = 2.0*cos(s)
do j = 1, ny
y = -1.0 + 2.0*(j-1)/(ny-1)
pxyz(i,j)%x = x*50
pxyz(i,j)%y = y*50
pxyz(i,j)%z = (z+1.0)*50
end do
end do !
! Set Hollow Fill Style
call gSetFacetFillStyle(GHOLLOW) !
! Compute spline surface after setting the spline tension
call gSetSplineTension(spten)
call gSetLineColour(GRED)
call gDrawSplineSurface(nx,ny,pxyz) !
! Draw control points mesh
call gSetLineColour(GBLACK)
call gSetLineWidth(1.0)
do i = 1, ny
call gMoveTo3D(pxyz(1,i)%x,pxyz(1,i)%y,pxyz(1,i)%z)
call gDrawPolylineTo3D(nx-2,pxyz(2,i))
end do
do i = 1, nx
call gMoveTo3D(pxyz(i,1)%x,pxyz(i,1)%y,pxyz(i,1)%z)
do j = 2, ny
call gDrawLineTo3D(pxyz(i,j)%x,pxyz(i,j)%y,pxyz(i,j)%z)
end do
end do
call gFlushGraphics !
! Close down
call gSuspendDevice
call gCloseGino
end
The basic Bezier surface is constructed from a grid of 3D control points, with an optional complexity specification of the final surface:
gDrawBezierSurface(nx, ny, mesh, [gUComp, gVComp])Where nx and ny are the dimensions of the 2 dimensional array of control points of type GPOINT3 passed in mesh.
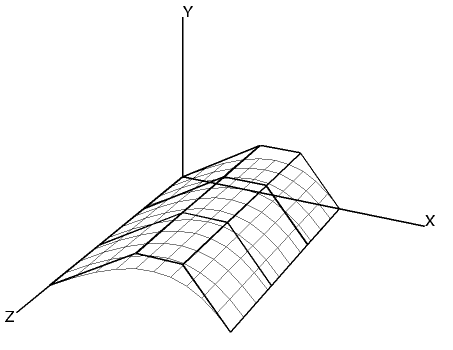 |
Bezier Surface |
Note that whilst only 16 control points are passed to the gDrawBezierSurface() routine, the surface consists of 100 (10x10) facets due to the default settings of gUComp and gVComp. This example is produced using the following code:
[C/C++] #include <gino-c.h>
#define NX 4
#define NY 4
GDIM paper;
GLIMIT3 viewport = {-200.0,200.0,-200.0,200.0,0.0,1000.0};
GLIMIT limits = {0.0,0.0,0.0,0.0}; /* Define control points */
GPOINT3 pxyz[NX][NY] = {
0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 50.0,
0.0, 0.0,100.0, 0.0, 0.0,150.0,
50.0,30.0, 0.0, 50.0,30.0, 50.0,
50.0,30.0,100.0, 50.0,30.0,150.0,
75.0,30.0, 0.0, 75.0,30.0, 50.0,
75.0,30.0,100.0, 75.0,30.0,150.0,
100.0, 0.0, 0.0,100.0, 0.0, 50.0, 100.0, 0.0,100.0,100.0, 0.0,150.0};
main() { int ip,i,j;
/* Initialize GINO and device */
gOpenGino();
xxxxx();
/* Set up 3D Viewport to fit whole drawing area */
gEnqDrawingLimits(&paper,&ip);
limits.xmax=paper.xpap;
limits.ymax=paper.ypap;
gSetViewport3D(&viewport,&limits);
/* Define Lighting and shading */
gSetShadingMode(GFLAT,0);
gSetLightSwitch(1,GON);
/* Define view */
gDefinePerspView(300.0,300.0,600.0,-0.3,-0.3,-0.6,800.0);
gUpdateView();
/* Set hollow fill style */
gSetFacetFillStyle(GHOLLOW);
/* Set material and draw surface */
gSetMaterialIndex(GDEFAULT,GDEFAULT);
gSetLineColour(GBLACK);
gDrawBezierSurface(NX,NY,&pxyz[0][0]);
/* Draw control points mesh */
gSetLineWidth(1.0);
for(i=0; i<NX; i++) {
gMoveTo3D(pxyz[i][0].x,pxyz[i][0].y,pxyz[i][0].z);
gDrawPolylineTo3D(NY,pxyz[i]);
}
for(i=0; i<NY; i++) {
gMoveTo3D(pxyz[0][i].x,pxyz[0][i].y,pxyz[0][i].z);
for(j=1; j<NX; j++)
gDrawLineTo3D(pxyz[j][i].x,pxyz[j][i].y,pxyz[j][i].z);
}
/* Close down */
gSuspendDevice();
gCloseGino();
}
[F90] use gino_f90
parameter (nx=4,ny=4)
type (GDIM) :: paper
type (GLIMIT3) :: viewport = &
GLIMIT3(-200.0,200.0,-200.0,200.0,0.0,1000.0)
type (GLIMIT) :: limits = GLIMIT(0.0,0.0,0.0,0.0) ! Define control points
type (GPOINT3) :: pxyz(nx,ny) = reshape( (/ &
GPOINT3( 0.0, 0.0, 0.0), GPOINT3( 50.0,30.0, 0.0), &
GPOINT3(75.0,30.0, 0.0), GPOINT3(100.0, 0.0, 0.0), &
GPOINT3( 0.0, 0.0,50.0), GPOINT3( 50.0,30.0,50.0), &
GPOINT3(75.0,30.0,50.0), GPOINT3(100.0, 0.0,50.0), &
GPOINT3( 0.0, 0.0,100.0), GPOINT3( 50.0,30.0,100.0), &
GPOINT3(75.0,30.0,100.0), GPOINT3(100.0, 0.0,100.0), &
GPOINT3( 0.0, 0.0,150.0), GPOINT3( 50.0,30.0,150.0), &
GPOINT3(75.0,30.0,150.0), GPOINT3(100.0, 0.0,150.0) /), &
(/nx,ny/) ) !
! Initialize GINO and device
call gOpenGino
call xxxxx
!
! Set up 3D Viewport to fit whole drawing area
call gEnqDrawingLimits(paper,ip)
limits%xmax=paper%xpap
limits%ymax=paper%ypap
call gSetViewport3D(viewport,limits) !
! Define Lighting and shading
call gSetShadingMode(GFLAT)
call gSetLightSwitch(1,GON)
!
! Define view
call gDefinePerspView(300.0,300.0,600.0,-0.3,-0.3,-0.6,800.0)
call gUpdateView !
! Set hollow fill style
call gSetFacetFillStyle(GHOLLOW)
!
! Set material and draw surface
call gSetMaterialIndex(GDEFAULT,GDEFAULT)
call gSetLineColour(GBLACK)
call gDrawBezierSurface(nx,ny,pxyz) !
! Draw control points mesh
call gSetLineWidth(1.0)
do i = 1, ny
call gMoveTo3D(pxyz(1,i)%x,pxyz(1,i)%y,pxyz(1,i)%z)
call gDrawPolylineTo3D(nx-1,pxyz(2,i))
end do
do i = 1, nx
call gMoveTo3D(pxyz(i,1)%x,pxyz(i,1)%y,pxyz(i,1)%z)
do j = 2, ny
call gDrawLineTo3D(pxyz(i,j)%x,pxyz(i,j)%y,pxyz(i,j)%z)
end do
end do
!
! Close down
call gSuspendDevice
call gCloseGino
stop
end
The tabulated Bezier surface is generated from a set of 3D control points and a vector. An intermediate Bezier curve is computed from the control points and the surface is constructed by extending the curve along the specified vector.
gDrawTabulatedBezierSurface(np, points, vector, [gUComp, gVComp])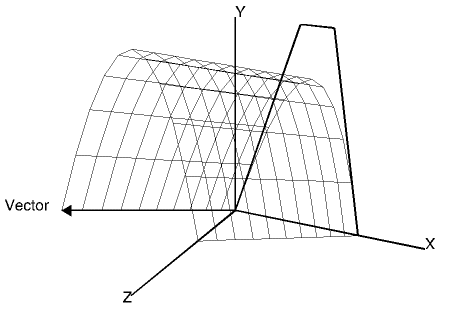 |
Tabulated Surface |
A swept Bezier surface is similar to the tabulated surface except that the surface is constructed along the curve computed from a second set of control points:
gDrawSweptBezierSurface(np1, points1, np2, points2, [gUComp, gVComp])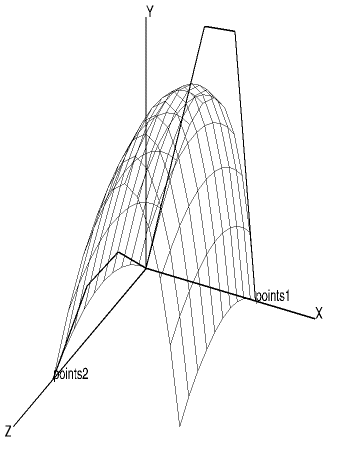 |
Swept Surface |
The ruled Bezier surface is also generated from two sets of 3D control points except that the surface is generated by constructing a grid of patches between each computed curve. The number of points in each set of control points need not be the same.
gDrawRuledBezierSurface(np1, points1, np2, points2, [gUComp, gVComp])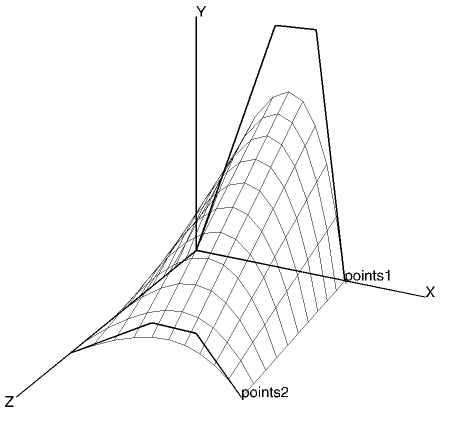 |
Ruled Surface |
A Bezier sphere is internally constructed by rotating a semi-circular Bezier curve around a central axis. The user needs only to specify the centre, radius and optionally its complexity and local orientation.
gDrawBezierSphere(xc, yc, zc, radius, [gUComp, gVComp, gURot, gVRot, gWRot,gUComp,gVComp])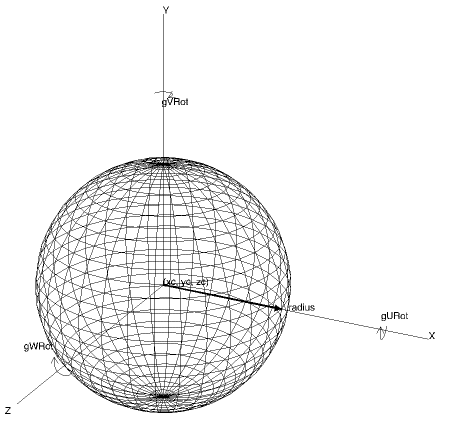 |
Bezier Sphere |
A Bezier volume of rotation is constructed from a user supplied set of 2D control points rotated round a central axis. The control points are used to generate a smooth Bezier curve which is rotated about a vector (0.0,1.0,0.0) starting at the position specified in xp,yp,zp. The optional arguments can be used to alter the complexity and local orientation.
gDrawBezierVolume(xp, yp, zp ,npts, points, [gURot, gVRot, gWRot, gUComp, gVcomp])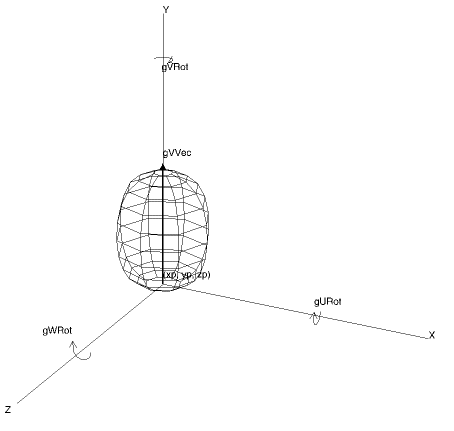 |
Bezier Volume |